Whether you work for a large research company or a small biotech startup, your goal is the same: effective lab management. But a lab can be a complicated space to manage. Keeping all the moving parts running efficiently can become overwhelming with many factors to consider.
Luckily, proven processes can help make lab management more straightforward, allowing you to focus on core objectives instead of getting bogged down by minor details. These systems will help you manage time and resources more efficiently and increase your lab’s productivity.
In this article, we'll reveal some of the most effective strategies to help you run an efficient lab without all the stress. We’ll discuss specific approaches to successful lab management and provide tips and pointers for implementing these systems.
Critical Steps to Effective Lab Management
The following are three crucial elements to successful modern labs:
- Master planning and prioritization
- Operate effective staff meetings
- Leverage document management software
Below, we look at each of these elements in detail.
Plan and Prioritize
A successful lab manager must be able to properly plan and prioritize. Knowing what needs to be done and which tasks take precedence will help you and your team improve productivity and maximize the use of limited resources. A huge component of this is effective time management, which involves managing the lab’s workflow by setting up an efficient schedule.
Aside from prioritizing the use of existing resources, it’s also necessary to determine where budgets should be spent. For example, it's easy to get lost in the hype of the various new technologies available on the market today. However, it’s crucial to prioritize what tools are best for your lab while staying within your budget.
Long-term planning is another critical area not to be overlooked. Focusing on short-term goals such as upcoming projects is essential, but an effective laboratory manager also looks ahead at longer-term needs. Some of the challenges that might require long-term planning include staff turnover, upgrading equipment to improve productivity, implementing new processes to increase throughput, and training employees to use new systems.
Tips for Planning and Prioritizing
Of course, prioritizing projects and allocating resources accordingly isn’t easy. Here are some tips for planning and prioritizing tasks for more effective lab management:
1. Identify Key Goals
Devising the right approach requires more than arbitrarily deciding what gets done and when. It requires acknowledging the purpose of each task and deciding which are the most essential factors, such as risks and associated costs. This enables you to assign the appropriate resources to tasks and align them with key objectives.
A crucial step here is identifying how your work aligns with the organization’s goals and understanding which initiatives have the largest impact.
A study by Clear Company found that “97% of employees and executives believe lack of alignment within a team impacts the outcome of a task or project.”
To overcome these barriers, managers must identify and consult project stakeholders and communicate with them effectively throughout a project. Internal stakeholders may include management team members, product and quality managers, technical services directors, department managers, etc. Of course, there are also external stakeholders to consider, such as research partners, vendors, and customers.
Need help staying on top of goals? Tools like Friday and ClickUp have built-in features that help you set high-level goals, break them down into smaller objectives, and keep track of your team’s progress.
2. Understand Scope and Metrics
The scope of a project refers to identifying precisely what is required at each stage and the expected outcomes. The main problem with a poorly defined scope is that managers may end up assigning too few resources to a project, leading to backlogs or missed deadlines. It can also lead to other issues, including time wasted on non-critical work and lack of enthusiasm from team members.
The laboratory manager should understand the full scope of each initiative and communicate this with all stakeholders. Each team member or project partner should precisely understand what is required and when.
Concerning scope, it’s also essential to know which metrics are required to track project success. For example, key performance indicators (KPI's) might relate to analytical cycle times, compliance with regulatory requirements, quality control, or customer satisfaction.
Many software options are available to help you track KPIs and project requirements. For example, most lab information management systems (LMS) such as Colabra offer built-in tools that enable you to track and analyze KPIs.
3. Assign Risk Factors
Risk is an inherent component of all initiatives. Some examples of risk include errors due to lack of training, failure to meet deadlines, and damage to equipment or samples. Identifying risks early and forging plans to mitigate them can greatly increase the chance of project success.
A laboratory manager should prioritize tasks, projects, and initiatives based on factors such as risk level (low, medium, high), category, resources required (personnel or financial), cost-benefit analysis, and alternatives considered.
There are tools available that can help streamline the risk analysis process, such as MasterControl and AuditBoard’s RiskOversight. These provide you with standardized methods for assessing risk, so that common language and protocols are used across the organization. They also enable you to compile all risk-assessment documentation and analyses in a single centralized platform that can be easily accessed whenever needed.
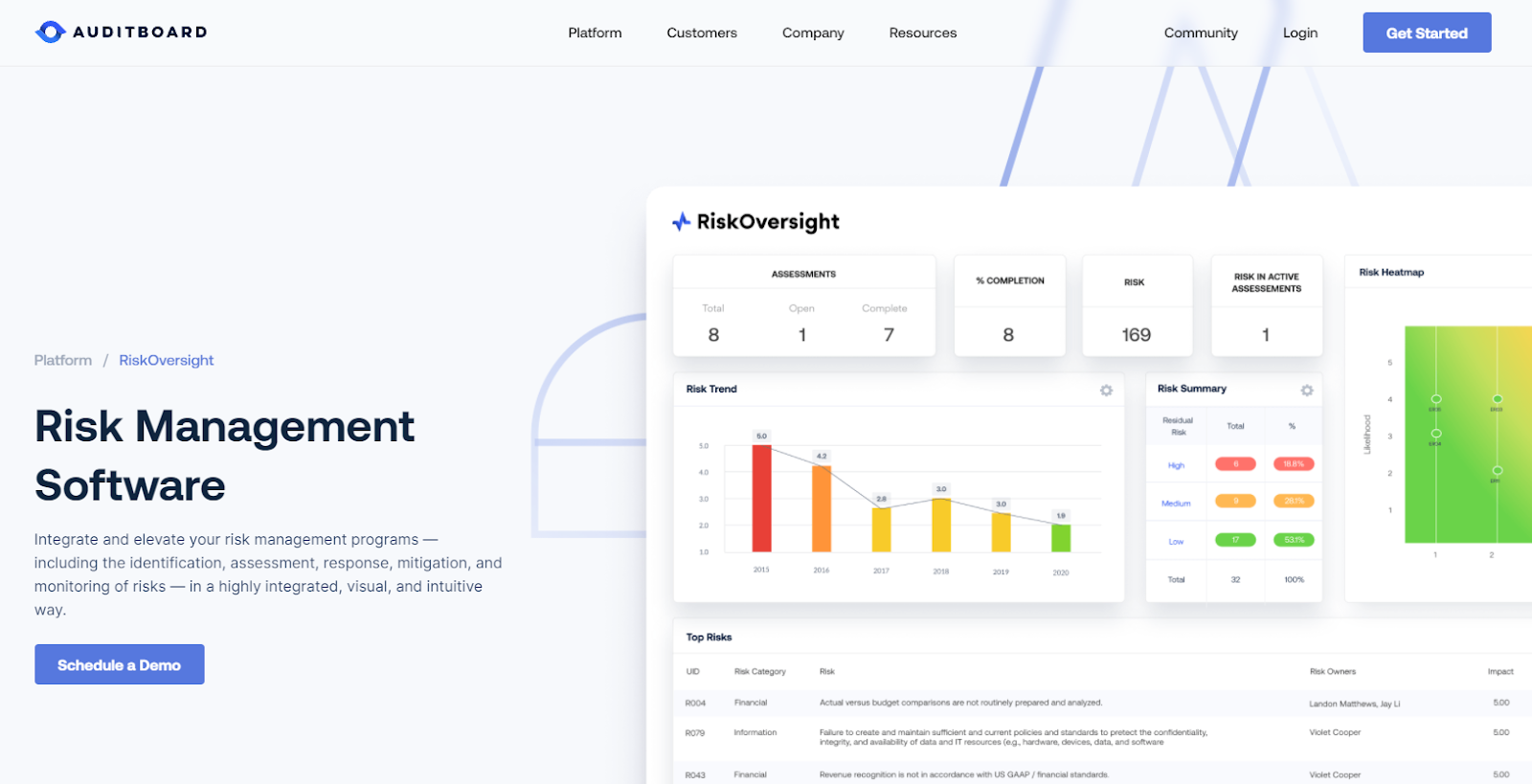
RiskOversight can help you identify, assess, and mitigate risks.
Run Effective Meetings
The ability to run effective staff meetings is considered a superpower in most industries and is certainly a vital tool for lab managers. While loathed by many, laboratory meetings are an essential activity that can impact productivity.
Meetings can:
- Improve engagement and collaboration
- Create a shared sense of purpose
- Provide a forum for efficient problem-solving and troubleshooting
- Help align groups and departments on project tasks
- Provide increased accountability for individuals and subgroups
- Facilitate discussions on appropriate measurements for success
- Nurture a positive environment and opportunities for personal growth
Of course, meetings also have downsides, including taking up valuable time and causing frustration for team members who don’t feel heard. When running effective meetings, managers often struggle with several factors, including managing time, encouraging participation, and delivering actionable outcomes.
Tips for Running Effective Meetings
Meeting leadership varies depending on the size and resources of the lab. However, the common goal is to achieve maximum results with the least effort. It takes some practice to learn how to be an effective lab meeting leader, but here are some tips for transforming staff meetings into a high-functioning management tool:
Set specific goals and objectives. When planning a meeting, ensure there is a real purpose to gathering team members and that all key objectives have been identified.
According to a 2019 Doodle study “more than a third (37%) of professionals consider unnecessary meetings to be the biggest cost to their organization.”
Prepare specific goals for your meeting and have an agenda ready (ideally distributed beforehand). Survey team members for topics or questions in advance to be added to the agenda.
Keep the team on task. While meetings provide an excellent forum to discuss the finer details of a project, it’s important not to get bogged down with the minutiae. Meetings should be kept brief and relevant to minimize their negative impact on productivity.
A good leader keeps the meeting on track, knows when to end it, and leaves attendees feeling that they have gained some value. You may even consider using a timer or stopwatch to ensure things stay on track.
Doodle analyzed the cost of poorly organized meetings and found that companies in the US lose a collective 16.64 billion hours and almost $400 billion per year.
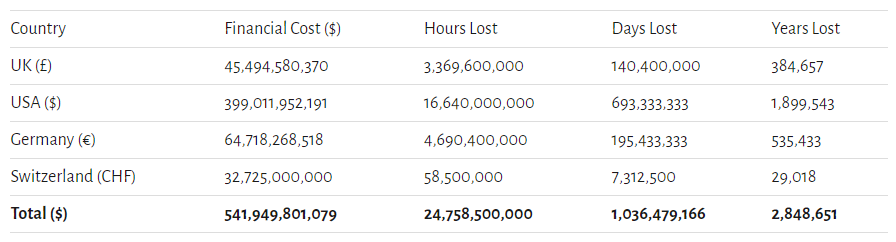
Source: Doodle
Of course, if you need to move or cancel a meeting, make sure to do so in ample time so that team members can organize their schedules accordingly.
Encourage participation and consensus. While meetings are necessary for group communication, they can also be great opportunities to develop employees and instill a sense of camaraderie. Encourage your team members to speak up and share their thoughts and avoid letting one or two members monopolize the discussion.
If possible, try to involve all attendees in any decisions that need to be made, rather than making those decisions yourself or among a few participants. If you want someone to share their opinion or results during the discussion, give them opportunities to do so by asking open-ended questions such as "What do you think?" instead of yes or no questions.
Improve meetings on an ongoing basis by asking attendees for feedback and ideas for future sessions.
Know your audience. Topics discussed at meetings should ideally be relevant to all attendees, and efforts should be made to ensure discussions are easily understood. For example, if you have newer team members, ensure they have the appropriate context for agenda items and avoid using company jargon that isn’t easily understood.
It’s also worth noting that including a morale boost at each meeting can hugely benefit the overall outcome and improve future attendance. Consider opening or closing the meeting by highlighting a recent achievement, such as reaching a project milestone.
That said, this shouldn’t turn into a full-blown status update—this happens to be the top source of annoyance among meeting attendees, according to Fellow: “Status updates are people’s #1 meeting pet peeve, followed by digressions and lack of preparation.”
Consider utilizing management software. If you’re a fan of using apps to streamline processes, you may want to take advantage of the various specialized meeting management software available. Meetin.gs is a handy tool that offers an easy-to-use interface, built-in notifications, communication app integrations, and the option to add agenda items. An alternative is nTask, a multi-tool project management platform that helps with meeting management and other tasks.
Meetin.gs offers a range of features to improve organization and productivity.
Utilize Document Management Systems
Managing the vast amount of data collected in lab projects can be challenging. Systems involving thousands of paper documents and boxes of files are still the norm in many labs where scientists waste time searching for data and often uncover illegible or unreliable information.
Lab document management systems (DMSs) provide a centralized solution for handling documents relating to laboratory work, helping ensure that all data is up-to-date, accessible, and compliant. There are various types of lab DMSs available, including electronic lab notebooks (ELNs), LIMSs, collaboration tools, and policy management software.
Modern document management systems offer a plethora of benefits, including:
- Saving time and resources: With data at their fingertips, scientists no longer have to spend precious time searching through files, folders, and boxes. From customizable experimental templates to searchable databases, document management systems have an ever-evolving roster of features to simplify daily routines and improve productivity.
- Holistic lens: Document management systems make it easy to view all relevant information for a given project in one place, providing a “big picture” perspective instead of a piecemeal view. Data and samples can be easily tracked through various project phases, making it easier to disseminate key information and draw appropriate conclusions.
- Avoid data loss: Physical storage systems are prone to data loss, theft, or damage, any of which could lead to dire consequences. Although not infallible, modern online systems are built with security in mind, so you can rest assured your data is well protected.
- Compliance: Document management systems provide laboratories with a comprehensive audit trail that can be used to track any file or document within your organization. Accurate reports and presentations can be produced quickly and easily without consulting with the whole team.
- Access tracking: These systems often allow you to track who has accessed or edited a particular file and when. This accountability helps to boost data security and avoid errors.
- Sharing and collaboration: Data from the entire team is pooled such that everyone who needs to access information can do so within a few clicks. This ensures all team members have full context and stay informed, enabling scientists to spend more time on novel discoveries instead of repeating work.
- Assign tasks and priorities: A common scenario in labs is that scientists create “busy work” due to not being assigned a specific task. A DMS can help organize projects and assign tasks and priorities so that personnel always know what they should be working on.
Perhaps most importantly, document management systems can improve overall morale within the organization. When team members are well-informed and organized, this leads to a greater sense of purpose and improved job satisfaction.
Choosing the Right Document Management Software
When choosing which document management systems to go with, there are several key elements you may want to look for, including:
- An intuitive interface for improved usability and a high acceptance rate. Colabra offers a modern, easy-to-navigate interface.
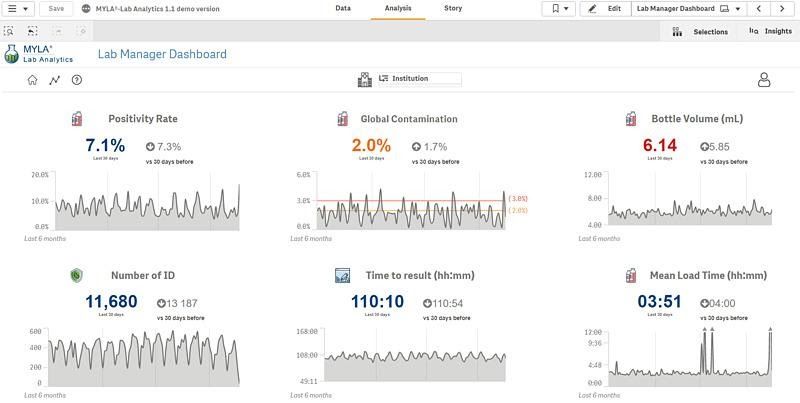
- Analytics features relevant to your specific objectives. MYLA Lab Analytics offers a variety of dashboards and modules designed specifically for microbiology laboratories.
- Sharing and collaboration tools that lab personnel can adopt easily. Colabra is an example of an ELN that puts a particular emphasis on collaboration. It enables admins to create experiments and assign them to specific team members. It also allows for real time editing, as well as commenting directly within the lab notebook to document results and discussions in one place.
- Integrations with other laboratory software to make editing and sharing documents simpler. For example, Colabra easily integrates with Google Sheets, Miro, Deepnote, and more.
- Notification features that enable team members to receive updates in real-time.
- Built-in compliance tools or integration opportunities. Colabra offers compliance functionalities with FDA Title 21 CFR Part 11 for operating in a regulated GxP environment, SOC 2 Type 2 certified for data protection, and regional standards like GDPR, ePrivacy, CCPA, LGPD, and PECR.
- Protocol and SOP management features. Colabra has an easy-to-use protocol creation tool.
- Easy-to-use data organization systems such as intuitive filing systems and tag managers. For example, Colabra enables you to search for data based on author, tag, project category, and other criteria.
Note that there is no one-size-fits-all solution, and the tools you decide to employ will depend heavily on your organization’s unique needs.
Implementing a Document Management System
DMS implementation consists of three core phases: planning, implementation, and evaluation.
Planning
As with the introduction of any new software, proper planning is critical. As discussed above, core steps in the planning process will be identifying fundamental goals, understanding the project’s scope, determining metrics, and assigning risk factors.
Key stakeholders such as the software provider, managers, and end-users should be heavily involved in the planning process. Ideally, end-users should be included in the early decision stage of the process when deciding which tools to adopt. As Salesforce found: “80% of knowledge workers want to be able to choose which tools they use to collaborate at work.”
Implementation
It’s important to remember that software installations don’t typically happen overnight, and the project will need to be managed over time. If proper planning and prioritization procedures have been followed, managing the project will be much easier. That said, managers should be prepared for bumps in the road, such as missed vendor deadlines or extended troubleshooting periods. Ensure that protocols are in place to discuss problems with the team, request input, and overcome issues.
A large component of managing this type of project is usually centered around training. Effective training protocols will help ensure successful software deployment, increased adoption, fewer problems encountered, and improved team morale. Vendors often offer a range of training options, including in-depth guides and train-the-trainer programs.
Evaluation
Deployment day doesn’t signal the end of the project. Document management system implementations require continuous monitoring and evaluation to ensure long-term success. Key metrics developed in the planning stage often include acceptance criteria such as adoption rates, satisfaction with the new tools, and productivity changes.
Key Takeaways
Lab management can be complex and, at times, overwhelming. But thankfully, there are many modern tools and processes available to help you keep the lab running as smoothly as possible. Consider these key strategies when looking for improvements in your organization:
- Master planning and prioritization
- Operate effective staff meetings
- Leverage document management systems
How are you planning to implement these solutions? Let us know in the comments below.